胡壮麟语言学教材修订版(3)
本站小编 免费考研网/2019-03-22
36. Distinguish the two possible meanings of “more beautiful flowers” by means of IC analysis. (北京第二外国语大学,2004)
VI. Analyze the following situation. (20%)
37. Draw a tree diagram according to the PS rules to show the deep structure of the sentence:
The student wrote a letter yesterday.
Key:
I.
1~5 DCDDD 6~10 ADDBA
II.
11~15 TTTTF 16~20 FTFTT
III.
21. simple 22. sentence
23. subject 24. predicate
25. complex 26. embedded
27. open 28. Adjacency
29. Parameters 30. Case
IV.
31. Syntax: Syntax refers to the rules governing the way words are combined to form sentences in a language, or simply, the study of the formation of sentences.
32. IC analysis: Immediate constituent analysis, IC analysis for short, refers to the analysis of a sentence in terms of its immediate constituents – word groups (phrases), which are in turn analyzed into the immediate constituents of their own, and the process goes on until the ultimate sake of convenience.
33. Hierarchical structure: It is the sentence structure that groups words into structural constituents and shows the syntactic category of each structural constituent, such as NP, VP and PP.
34. Trace theory: After the movement of an element in a sentence there will be a trace left in the original position. This is the notion trace in T-G grammar. It’s suggested that if we have the notion trace, all the necessary information for semantic interpretation may come from the surface structure. E.g. The passive Dams are built by beavers. differs from the active Beavers built dams. in implying that all dams are built by beavers. If we add a trace element represented by the letter t after built in the passive as Dams are built t by beavers, then the deep structure information that the word dams was originally the object of built is also captured by the surface structure. Trace theory proves to be not only theoretically significant but also empirically valid.
V.
35.
An endocentric construction is one whose distribution is functionally equivalent, or approaching equivalence, to one of its constituents, which serves as the center, or head, of the whole. A typical example is the three small children with children as its head. The exocentric construction, opposite to the first type, is defined negatively as a construction whose distribution is not functionally equivalent to any of its constituents. Prepositional phrasal like on the shelf are typical examples of this type.
36.
(1) more | beautiful flowers
(2) more beautiful | flowers
VI.
S
NP VP
Det. NP V NP Adv.
Det. N.
The student wrote a letter yesterday.
Chapter 5 Meaning
[Mainly taken from lxm1000w’s exercises. – icywarmtea]
I. Choose the best answer. (20%)
1. The naming theory is advanced by ________.
A. Plato B. Bloomfield C. Geoffrey Leech D. Firth
2. “We shall know a word by the company it keeps.” This statement represents _______.
A. the conceptualist view B. contexutalism
C. the naming theory D. behaviorism
3. Which of the following is NOT true?
A. Sense is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form.
B. Sense is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form.
C. Sense is abstract and decontextualized.
D. Sense is the aspect of meaning dictionary compilers are not interested in.
4. “Can I borrow your bike?”_______ “You have a bike.”
A. is synonymous with B. is inconsistent with
C. entails D. presupposes
5. ___________ is a way in which the meaning of a word can be dissected into meaning components, called semantic features.
A. Predication analysis B. Componential analysis
C. Phonemic analysis D. Grammatical analysis
6. “Alive” and “dead” are ______________.
A. gradable antonyms B. relational antonyms
C. complementary antonyms D. None of the above
7. _________ deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.
A. Reference B. Concept C. Semantics D. Sense
8. ___________ refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form.
A. Polysemy B. Synonymy C. Homonymy D. Hyponymy
9. Words that are close in meaning are called ______________.
A. homonyms B. polysemies C. hyponyms D. synonyms
10. The grammaticality of a sentence is governed by _______.
A. grammatical rules B. selectional restrictions
C. semantic rules D. semantic features
II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)
11. Dialectal synonyms can often be found in different regional dialects such as British English and American English but cannot be found within the variety itself, for example, within British English or American English.
12. Sense is concerned with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience, while the reference deals with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form.
13. Linguistic forms having the same sense may have different references in different situations.
14. In semantics, meaning of language is considered as the intrinsic and inherent relation to the physical world of experience.
15. Contextualism is based on the presumption that one can derive meaning from or reduce meaning to observable contexts.
16. Behaviorists attempted to define the meaning of a language form as the situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth in the hearer.
17. The meaning of a sentence is the sum total of the meanings of all its components.
18. Most languages have sets of lexical items similar in meaning but ranked differently according to their degree of formality.
19. “It is hot.” is a no-place predication because it contains no argument.
20. In grammatical analysis, the sentence is taken to be the basic unit, but in semantic analysis of a sentence, the basic unit is predication, which is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence.
III. Fill in the blanks. (20%)
21. __________ can be defined as the study of meaning.
22. The conceptualist view holds that there is no __________ link between a linguistic form and what it refers to.
23. __________ means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.
24. Words that are close in meaning are called __________.
25. When two words are identical in sound, but different in spelling and meaning, they are called __________.
26. __________ opposites are pairs of words that exhibit the reversal of a relationship between the two items.
27. __________ analysis is based upon the belief that the meaning of a word can be divided into meaning components.
28. Whether a sentence is semantically meaningful is governed by rules called __________ restrictions, which are constraints on what lexical items can go with what others.
29. A(n) __________ is a logical participant in a predication, largely identical with the nominal element(s) in a sentence.
30. According to the __________ theory of meaning, the words in a language are taken to be labels of the objects they stand for.
IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)
31. Entailment
32. Proposition
33. Componential analysis
34. Reference
V. Answer the following questions. (20%)
35. What are the sense relations between the following groups of words?
Dogs, cats, pets, parrots; trunk, branches, tree, roots (青岛海洋大学,1999)
36. What are the three kinds of antonymy? (武汉大学,2004)
VI. Analyze the following situation. (20%)
37. For each group of words given below, state what semantic property or properties are shared by the (a) words and the (b) words, and what semantic property or properties distinguish between the classes of (a) words and (b) words.
(1) a. bachelor, man, son, paperboy, pope, chief
b. bull, rooster, drake, ram
(2) a. table, stone, pencil, cup, house, ship, car
b. milk, alcohol, rice, soup
(3) a. book, temple, mountain, road, tractor
b. idea, love, charity, sincerity, bravery, fear (青岛海洋大学,1999)
Key:
I.
1~5 ABDDB 6~10 CACDA
II.
11~15 FFTFT 16~20 TFTTT
III.
21. Semantics 22. direct
23. Reference 24. synonyms
25. homophones 26. Relational
27. Componential 28. selectional
29. argument 30. naming
IV.
31. Entailment: It is basically a semantic relation (or logical implication), and it can be clarified with the following sentences:
a. Tom divorced Jane.
b. Jane was Tom’s wife.
In terms of truth value, the following relationships exist between these two sentences: when A is true, B must be also true; when B is false, A must also be false. When B is true, A may be true or false. Therefore we can say A entails B.
32. Proposition: It is the result of the abstraction of sentences, which are descriptions of states of affairs and which some writers see as a basic element of sentence meaning. For example, the two sentences “Caesar invaded Gaul” and “Gaul was invaded by Caesar” hold the same proposition.
33. Compositional analysis: It defines the meaning of a lexical element in terms of semantic components, or semantic features. For example, the meaning of the word boy may be analyzed into three components: HUMAN, YOUNG and MALE. Similarly girl may be analyzed into HUMAN, YOUNG and FEMALE.
34. Reference: It is what a linguistic form refers to in the real world; it is a matter of the relationship between the form and the reality.
V.
35.
Hyponymy, metonymy or part-whole relationship
36.
(Omit.)
VI.
37.
(1) The (a) words and (b) words are male.
The (a) words are human, while the (b) words are non-human.
(2) The (a) words and (b) words are inanimate.
The (a) words are instrumental, while the (b) words are edible.
(3) The (a) words and (b) words are worldly or conceptual.
The (a) words are material, while the (b) words are spiritual.
Chapter 7 Language, Culture and Society
[注:第六章无测试题]
I. Choose the best answer. (20%)
1. _______ is concerned with the social significance of language variation and language use in different speech communities.
A. Psycholinguistics B. Sociolinguistics
C. Applied linguistics D. General linguistics
2. The most distinguishable linguistic feature of a regional dialect is its __________.
A. use of words B. use of structures
C. accent D. morphemes
3. __________ is speech variation according to the particular area where a speaker comes from.
A. Regional variation B. Language variation
C. Social variation D. Register variation
4. _______ are the major source of regional variation of language.
A. Geographical barriers
B. Loyalty to and confidence in one’s native speech
C. Physical discomfort and psychological resistance to change
D. Social barriers
5. _________ means that certain authorities, such as the government choose, a particular speech variety, standardize it and spread the use of it across regional boundaries.
A. Language interference B. Language changes
C. Language planning D. Language transfer
6. _________ in a person’s speech or writing usually ranges on a continuum from casual or colloquial to formal or polite according to the type of communicative situation.
A. Regional variation B. Changes in emotions
C. Variation in connotations D. Stylistic variation
相关话题/语言学
语言学概论复习笔记
《语言学概论》复习笔记 一、语言和语言学 1.语言的本质 (1)自然属性:语言从本质上来说是一套符号系统。 (2)社会属性:是人类最重要的交际工具。 (3)心理属性:是人类进行思维的工具。 语言的自然属性从本质上来说是一套 符号 系统。(99年填空) 2.什么是符号?语言符号和其它符号的不同特点。 符号:用 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-03-21胡壮麟语言学术语英汉对照翻译表
胡壮麟语言学术语英汉对照翻译表 1. 语言的普遍特征: 任意性arbitrariness 双层结构duality 既由声音和意义结构 多产性productivity 移位性displacement:我们能用语言可以表达许多不在场的东西 文化传播性cultural transmission 2。语言的功能: 传达信息功能informative 人济功能:interpersonal 行事功能: ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-03-20胡壮麟语言学教程大纲分析及试题
胡壮麟《语言学教程》(修订版) 学习指导 第二部分 重点章节测试题 Test One: Invitations to Linguistics I. Choose the best answer. (20%) 1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human __________. A. contact B. communication C. relation ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-03-17语言学纲要学习指导书练习答案(整理版)
《语言学概论》学习辅导书参考答案(导言) 一、名词解释(20分,每小题4分) 1.语言学:就是以语言为研究对象的科学,研究语言的本质、语言的结构和发展规律。 2.小学:指我国传统的语文学,包括文字学、音韵学、训诂学三方面的内容。 3.专语语言学:也叫具体语言学、个别语言学,以一种(或几种有联系的)语言 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-02-13华师语言所学硕2019年语言学概论考研真题
一、填空题所谓递归性,是指相同的结构规则可以( ),可以由( )扩展成层层嵌套的( )。语言系统可以分为( )、( )、( )等子系统。黏着语又称( ),其特点是通过附加多种( )来表示各种( )。音质的不同取决于三方面的条件:一是( ),二是( ),三是( )的形状。根据义项之间不同的关 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-01-03丁言仁《英语语言学纲要》笔记和课后习题详解
目录封面内容简介目录第1章 我们身边的语言 1.1 复习笔记 1.2 课后习题详解第2章 英语语法 2.1 复习笔记 2.2 课后习题详解第3章 英语语音系统和书写系统 3.1 复习笔记 3.2 课后习题详解第4章 英语语义和词汇 4.1 复习笔记 4.2 课后习题详解第5章 语言在语境中的应用 5 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30扬州大学文学院816语言学理论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2014年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2015年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2016年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2017年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2018年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题内容简介本书收录了扬州大学文学院&ldq ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30江西师范大学文学院语言学概论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2012年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2013年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2014年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2015年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2016年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2017年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题内容 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30日本语言学校介绍及之后的升学之路
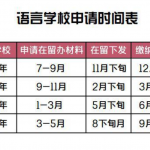 随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-18
随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-182019年北京邮电大学817英语语言学与文学基础考研大纲
817英语语言学与文学基础一、考试要求要求考生系统地掌握大学本科期间所学的语言学概论和英美文学的基本概念和知识,并且语言学方向考生能够运用语言学基本规则和理论分析一般的语言现象,文学方向考生能够运用所学知识对作家、作品和文学人物进行初步的分析、批判。二、考试内容语言的概念、特征以及各分支的概念、研究 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学概论和现代汉语考研初试大纲
《语言学概论和现代汉语》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段现代汉语和语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学理论考研初试大纲
《语言学理论》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能力,并由此判断学生是否具有进一步深造的基本素质和 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年华侨大学810语言学概论考研初试大纲
2019年华侨大学硕士研究生招生考试初试自命题科目考试大纲招生学院: 华文学院 招生专业: 华语与华文教育科目名称: 语言学概论一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为150分,考试时间为180分钟。(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸( ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-04
